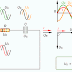
Lenz's Law
When the current through a coil changes, a voltage is induced. Lenz's Law states that the polarity of the induced voltage always opposes
the change in current that caused it. The diagram above illustrates
this law. When the switch closes, the current tries to increase, and the
magnetic field starts expanding. The expanding magnetic field induces a
voltage, which opposes an increase in current. So, at the instant of
switching, the current remains the same. When the rate of expansion
decreases, the induced voltage decreases, allowing the current to
increase. As the current reaches a constant value, there is no induced
voltage.
The diagram illustrates the direction of induced voltage when the
current is switched off. In a steady-state condition, the current has a
constant value. There is no induced voltage because the magnetic field
is unchanging. If the switch is opened, the current tries to reduce, and
the magnetic field begins to collapse. At the time of switching, the
induced voltage has a direction that prevents any decrease in current.
The current remains the same as prior to the switch opening. When the
rate of collapse decreases, induced voltage decreases, allowing current
to decrease to zero value.






.gif)



No comments:
Post a Comment